Lower back pain is one of the most common reasons working-age people see a neurologist.According to statistics, nine out of ten people experience low back discomfort at least once in their lives, and about 9% of cases result in disability.The first episode is usually recorded before the age of 30.From age 30 to 60, the risk increases.
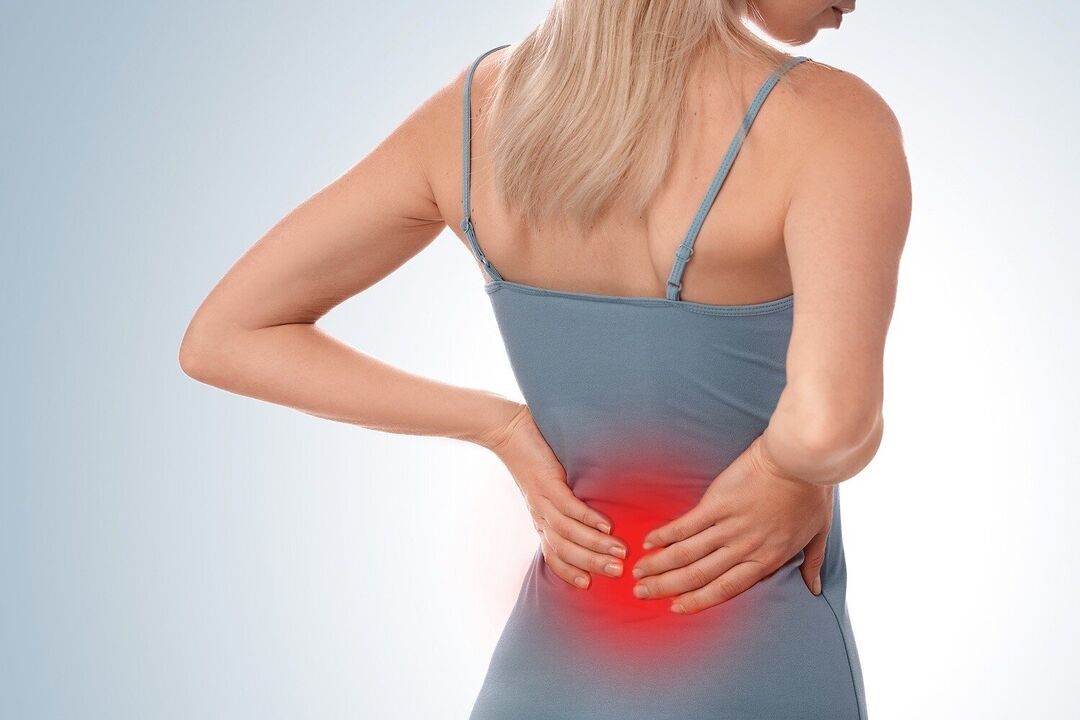

Unfortunately, young people don't always heed the warning signs.Many people believe that back pain is caused by overexertion, physical activity, or sitting in front of a computer for long periods of time.But in fact, it can be a symptom of a serious illness.Low back pain can be caused by a variety of conditions: from spinal problems to kidney failure.Only a timely visit to your doctor can help determine the cause and provide the correct treatment.
Possible causes of lower back pain: What hurts?
ankylosing spondylitis
Lumbar pain syndrome occurs when the vertebrae fuse into large pieces.Loss of mobility in the lower back.With ankylosing spondylitis, calcium deposits are also seen in the ligaments that support the spine, which can also cause pain when trying to turn, stand, or perform any other movement.
Unique symptoms of pathology:
- Stiffness in body movements of the waist;
- The pain worsens after prolonged periods of immobility, especially after a night's sleep.
osteochondrosis
The disease manifests itself as thinning of the spinal discs.As a result, the shock-absorbing function of the spine is reduced, the nerve roots are squeezed, and the muscles around the affected area spasm.The person will feel severe pain.If left untreated, osteochondrosis can progress, leading to herniation and disc herniation.The protrusion of cartilage tissue compresses the spinal cord.Not only does the person suffer from severe low back pain, but the nerve supply to the lower limbs is also disrupted.
Significant symptoms of osteochondrosis:
- Pain worsens when trying to roll from back to abdomen, rising from a horizontal or seated position, or bending over;
- Patients often report weakness and numbness in one or both legs.
spondyloarthropathy
The lower back can be injured due to degenerative changes in the cartilage tissue covering the intervertebral discs.The elastic layer becomes thinner and osteophytes (hard bony structures) appear in their place.The distance between vertebrae decreases with simultaneous compression of the spinal canal.
Nature of Spondyloarthropathic Pain:
- Accompanied by limited spinal mobility in the lower back until continued stiffness;
- The condition worsens after walking, sitting, standing, and other stress;
- Radiates to the pelvic area and thighs.
Urolithiasis
Pathological attacks manifest themselves as severe pain in the back on the side of the affected kidney.The severity and nature of the sensation do not change based on the position of the body.The patient cannot find an easier position than this.
Urolithiasis attacks are accompanied by other specific symptoms:
- lower back pain;
- Reduction in urine volume, change in color, and presence of blood impurities;
- Pain during urination;
- Body temperature may increase due to inflammation.
Other causes of lower back pain and spasms
Low back pain syndrome can be observed in the following conditions:
- Pregnancy, including early pregnancy;
- Dysmenorrhea in women;
- osteomyelitis;
- appendicitis;
- inflammation of the pancreas;
- Intestinal lesions;
- Back injuries;
- Lumbar tumors;
- Inflammatory processes in female reproductive organs;
- Male prostatitis, etc.
Expert opinion
Low back pain: What to do?Do not make sudden movements, especially if you are in pain from a fall or blow.Try to assume the most comfortable position.If the pain is severe and does not subside after changing positions, call an ambulance - it is most likely renal colic and will require hospitalization.In other cases, you can use ointments and pills to provide relief.Contact an expert as soon as possible.Doctors can help relieve even severe pain and prescribe treatments.
Diagnosis of low back pain
During the first visit, your doctor may prescribe a blockade to relieve acute pain.When the patient feels better, the doctor will perform a more thorough examination and take a medical history.It is important to figure out the location, nature, duration of pain, factors that make it worse or, conversely, improve health.Doctors will ask about past injuries and illnesses starting in early childhood.A medical history can help illustrate the cause of back pain and which diagnostic procedures can provide a more complete picture.
Your doctor may prescribe:
- General analysis of urine and blood.Based on the results, they diagnose inflammatory processes, determine signs of pathology in the kidneys and digestive organs;
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys and urinary system.If urolithiasis is suspected, testing is needed.Doctors use ultrasound to determine the location and extent of the inflammatory process and assess the size of the stones in order to correctly develop a treatment strategy;
- Lumbar spine X-ray.These images help determine pathological conditions in the vertebrae and adjacent tissues.To clarify X-rays, CT or MRI are additionally prescribed - these are more informative examination methods;
- Ultrasound examination of pelvic organs.When women experience low back pain, it may indicate endometritis or salpingo-oophoritis.Pregnant women must undergo examination to determine the tone of the uterus;
- Prostate ultrasound.If a man experiences lower back pain, it may be a sign of inflammation or prostate cancer.Doctors perform TRUS to determine the structure of the glands.
After a general examination, your doctor may prescribe a more targeted treatment plan.In some cases, consultation with surgeons, therapists, gynecologists, and other specialists is required to confirm the diagnosis.
Low back pain treatment
Treatment is completely individualized.The doctor begins treating a patient when he has received the most complete information about the patient's condition or at least has data to suggest a diagnosis.The treatment of renal colic and osteochondrosis is fundamentally different.
drug treatment
To relieve pain, NSAIDs are most commonly prescribed in the form of injections, ointments, and tablets.These medications help quickly relieve inflammation and muscle spasms.NSAIDs can have side effects, so doctors accurately calculate the dose and course duration for each patient.
If low back pain treatment doesn't work within 2-3 days, your doctor will opt for hormonal medications.Medications are only needed to relieve acute conditions.Antispasmodics, decongestants, and B vitamins are used as adjunctive medications.If the patient experiences low back pain or pain when urinating, antibiotics may be an option.Your doctor will tell you why you need this or that medicine and how to take it correctly.
non-pharmacological treatment
The procedure is performed in separate sessions after the exacerbation of the condition resolves.In complex pain management, the following methods are used:
- Physical therapy: radiofrequency neuromodulation, electrophoresis, phonophoresis, magnetic therapy;
- Physical therapy: A set of daily exercises chosen by a doctor, practiced in a swimming pool;
- Massage: treatment of the lower back and buttocks and general strengthening;
- Acupuncture, leech therapy and other treatments.
surgical treatment
Follow the instructions strictly.If the patient experiences low back pain and the body temperature does not drop while taking the medicine, the inflammatory focus needs to be removed.For tumors and metastases, radical intervention is required.
If there are lesions in the female reproductive organs and pain in the lower abdomen, diagnostic dilation and curettage and laparoscopy are required.If medications fail to clear urolithiasis, patients may also need surgery.
You cannot tolerate the pain and discomfort in your lower back.Your body will send you signals that you need to pay attention to that area.